 By Pasha Yuen
By Pasha Yuen
Please Click Here for Part 1
Human Genetic Resources (HGR) regulations in China aim to protect the genetic information of the Chinese population, by preventing this information from being exported for illegal activities. Even if you have a clear purpose for such materials you need to obtain specific approval before you can carry out any clinical trials in China.
Which samples fall under HGR?
HGR refers to the materials that could potentially carry genetic information from an individual. The regulations specify the types of materials from which HGR can be extracted, including:
- Cells
- Whole blood
- Tissue or tissue sections
- Semen
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- Thoracic or abdominal fluid
- Bone marrow smear
- Hair with follicles
- …and others
The collection and storage of these materials are tightly regulated by the HGR legislation. Originally managed by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), the management HGR activities are now being supervised by the National Health Commission (NHC), effective as of 1st May 2024. Under the new changes, all relevant activities that make use of HGR from Chinese patients or volunteers in clinical trials would be managed by the NHC.
Regulatory Organisations
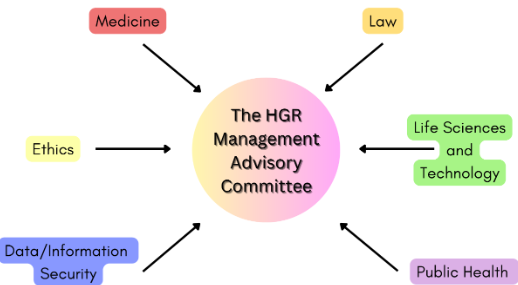
Different institutions and departments collaborate to ensure the legislation is effectively executed. The NHC is responsible for the regulation of HGR legislation. Regional regulations are split amongst provincial-level administration departments for daily management, investigations, and inspections. External consultation and technical support are provided by an advisory committee with expertise from different sectors.
The following diagram summarises the input from different parties in HGR regulations.
 Foreign Parties
Foreign Parties
In the past there was some confusion whether organisations fell under this regulation if they were based in or had a presence in China. Therefore, effective from July 2023, the most recent updates on the HGR regulations provided a clearer definition of “foreign party”:
“Foreign Party”
- An overseas individual or organisation holding or indirectly holding over 50% of shares, equity, voting rights, property shares or other similar rights.
- An overseas individual or organisation holding or indirectly holding under 50% of holdings, but their voting rights or other rights dominate or exert significant influence on management or decision-making.
- An overseas individual or organisation that is investing, has mutual agreements/ other arrangements that dominate or exert significant influence on management or decision-making.
- Other circumstances under laws, administrative regulations, or rules by competent authorities.
Preparation in advance of clinical trials in China
All foreign parties should apply for a permit for all types of activities involving HGR collection in China. Different types of licenses were designed that cater for the various usages of genetic resources from the Chinese population.
In our next and final blog of this series, we will explain the different types of licensing and provide step-by-step guidance on the application process.